Finding the right 3D printer cartridge heater can feel like a guessing game. Get it wrong, and you risk poor prints or even damaging your machine. Don't let your next project fail because of a bad choice.
The best 3D printer cartridge heater perfectly matches your hotend's diameter and length, operates at the correct voltage, delivers adequate wattage (typically 30-40W), and features durable construction like a 304 stainless steel casing with high-temperature fiberglass wiring for reliable, long-term performance.
Choosing the right heating element is key to consistent 3D printing. Over the years, I have seen many people struggle with inconsistent temperatures or even burned-out heaters. Let me share how to make the best choice.
What Diameter Cartridge Heater Do You Need?
A loose heater means poor heat transfer and slow heating. Too tight, and it might not even fit into your hotend block. Do you know the exact fit your hotend needs?
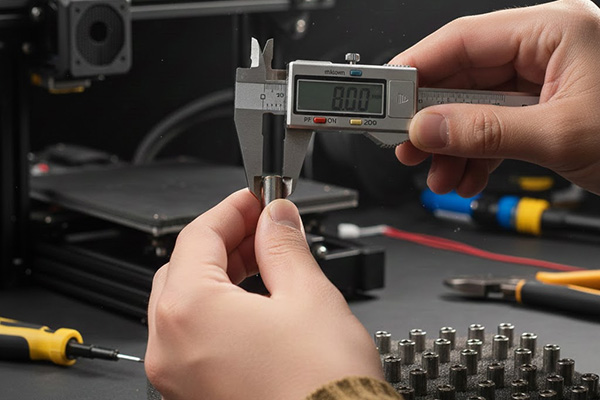
The correct diameter for your 3D printer cartridge heater is critical for efficient heat transfer and proper fit. Most 3D printer hotends use either 6mm or 8mm diameter cartridge heaters. Measure your hotend's bore precisely to ensure a snug, effective fit.
Why Diameter is So Important for Your Hotend
I once watched a friend try to force an 8mm heater into a 6mm hotend block. It did not go well. The wrong diameter creates many problems. A heater that is too small leaves an air gap. Air is a poor conductor of heat. This means your heater works harder but heats less effectively. You will see slower heat-up times and less stable temperatures. A heater that is too big will not fit. It is that simple. This is why precision is not just a nice-to-have, but a must-have for these components.
At ELEKHEAT, we understand the need for exact dimensions. We manufacture heaters that meet precise tolerances for various industrial and commercial uses. When you select a cartridge heater, always confirm the diameter. A good fit ensures optimal thermal contact. This allows the heater to transfer heat directly and efficiently to your hotend. This direct transfer leads to faster heating. It also creates a more stable temperature during printing. This means better print quality.
Common Cartridge Heater Diameters
| Diameter (mm) | Common Usage | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| 6 mm | Standard for many desktop 3D printers; often paired with 12V/24V systems. | Good for compact hotends; requires precise bore for optimal thermal contact. |
| 8 mm | Used in larger or more powerful hotends, sometimes for industrial 3D printers. | Offers more heating surface area; can provide higher wattage in some cases. |
Always measure the hole in your hotend block. Use digital calipers for the best accuracy. Do not guess the size. A perfect fit directly impacts your print quality.
Why Does Cartridge Heater Length Matter?
You might think a longer heater means more heat, but that is not always true. A heater that is too long or too short for your hotend can cause real problems. Do you know how length affects your heating performance?
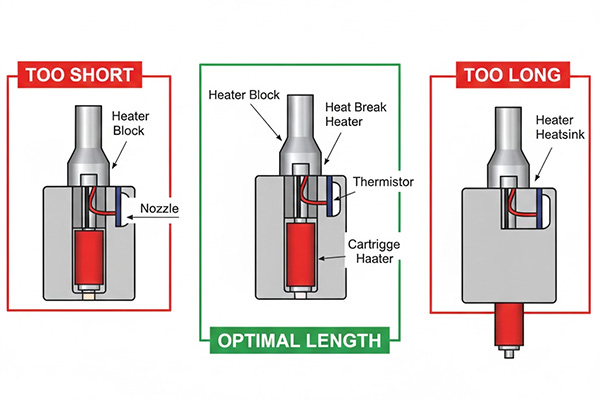
The length of your 3D printer cartridge heater matters because it needs to fit within the heated zone of your hotend block. A heater that is too long will extend beyond the block, wasting energy. A heater that is too short will not provide uniform heating.
How Heater Length Impacts Temperature Uniformity
I learned this the hard way during a prototype build. I had a heater that was slightly too long. The part sticking out just radiated heat into the air around the hotend. This made my print cooling fan less effective. It also made the area around my print warmer than it should have been. This impacted my print's overhangs and bridging performance. The opposite problem, a heater that is too short, creates cold spots in your hotend. This leads to inconsistent melting of the filament. Both situations mean poor print quality and wasted energy.
The heater's active heating section must sit entirely within the metal hotend block. If it is too long, the exposed part loses heat to the ambient air. This reduces efficiency. It also means your PID tuning will be harder. If the heater is too short, it will not heat the entire hotend block evenly. This creates temperature gradients. These gradients cause issues like filament clogging or inconsistent extrusion. We design our tubular heaters for even heat distribution. This ensures that every millimeter of the heating element is utilized effectively within its intended application.
Matching Heater Length to Your Hotend
- Measure the depth of the bore in your hotend block.
- Choose a heater with an active heating length that matches this depth.
- Consider the lead wires. Make sure the wires exit the block without bending too sharply.
A properly sized heater ensures all its heat output goes into warming the hotend. This gives you consistent extrusion temperatures. This helps your 3D prints come out exactly as you designed them.
How Much Power Should Your Cartridge Heater Have?
Ever waited forever for your printer to reach temperature? Or worse, had it struggle to hold heat during a fast print? This often comes down to wattage. Is your heater powerful enough for your needs?
Your 3D printer cartridge heater should typically have 30W to 40W of power. This range offers a good balance between fast heat-up times and stable temperature control for most standard desktop 3D printers. Too little wattage means slow heating, while too much can overwhelm your printer's power supply.
Wattage and Performance: Finding the Sweet Spot
I remember upgrading an old 3D printer. It came with a low-wattage heater. It took ages to heat up, and printing ABS was a nightmare. I switched to a 40W heater of the same size. The difference was night and day. Heat-up times cut in half. Temperature stability improved dramatically, even at higher print speeds. This showed me how critical wattage is for both speed and consistency.
Wattage directly affects how quickly your hotend heats up and how well it maintains temperature. For most desktop 3D printers, 30W to 40W is a suitable range. A 30W heater provides a good balance for many setups. It heats up reasonably fast and maintains temperature well. A 40W heater will heat up faster. It also has more "reserve" power to keep the temperature stable, even when filament is flowing quickly. This is crucial for consistent extrusion.
However, more wattage is not always better. Going too high, for example, 50W or 60W, might overload your printer's power supply or mainboard. This can cause damage. Always check your printer's specifications to ensure it can handle the chosen wattage. We produce various types of tubular heaters and cartridge heaters. We focus on energy efficiency and performance. Our designs ensure that the rated wattage delivers optimal heat output without unnecessary power draw.
Choosing the Right Wattage
| Wattage | Heat-up Speed | Temperature Stability | Power Supply Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25W | Slow | Moderate | Good for smaller, less demanding setups; very low risk of overload. |
| 30W | Moderate | Good | Standard for many basic hotends; balanced performance. |
| 40W | Fast | Excellent | Recommended for faster printing, exotic filaments; check PSU capacity. |
| 50W+ | Very Fast | Superior | For specialized, high-flow systems; requires robust power supply and mainboard. |
Consider your typical print speeds and the types of filaments you use. If you print fast or with high-temp materials, a 40W heater offers significant benefits.
Is 12V or 24V Better For Your 3D Printer Heater?
Connecting a 12V heater to a 24V system, or vice-versa, is a common and dangerous mistake. It can lead to instant failure or even fire. Do you know which voltage your 3D printer uses for its hotend?
You must match the voltage of your 3D printer cartridge heater to your printer's power supply (PSU) output for the hotend. Most modern 3D printers use 24V systems, while older or smaller machines might use 12V. Using the wrong voltage will lead to either underperformance or immediate burnout.
The Critical Importance of Voltage Matching
I once saw a colleague plug a 12V heater into a 24V printer during a late-night assembly. There was a pop, a flash, and a small puff of smoke. The heater was instantly destroyed. This is not just about replacing a part; it is about safety. Mismatched voltage can overload components. It can create fire hazards. This is why always double-check the voltage requirement.
Voltage is not something you can guess. It is a fundamental electrical specification that must match your printer's system. If you connect a 12V heater to a 24V power supply, the heater will draw four times the intended power. This will cause it to overheat and burn out almost instantly. It can also damage your mainboard's MOSFET, which controls the heater. Conversely, a 24V heater connected to a 12V supply will only draw one-quarter of its rated power. It will barely heat up at all.
Always check the label on your printer's power supply or mainboard. It will clearly state whether it outputs 12V or 24V for the hotend. Our diverse range of heating elements, including single-head tubes and heating coils, comes in various voltage specifications to meet exact customer requirements. This prevents such costly and dangerous mistakes.
Voltage Options and Your Printer
| Voltage | Common Printer Types | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | Older, smaller desktop printers (e.g., some Anet, older Creality Ender 3). | Lower power draw (generally), simpler circuits. | Thicker wires needed for same power; slower heat-up for higher wattages. |
| 24V | Most modern desktop 3D printers (e.g., Prusa, newer Creality Ender 3). | Thinner wires possible for same power; faster heat-up times; more efficient. | Higher voltage requires careful handling; instant burnout with 12V heaters. |
Always verify your printer's voltage before buying any heating element. This simple step saves you time, money, and potential hazards.
What Materials Make a Reliable Cartridge Heater?
Have you ever had a heater's wires become brittle or its casing corrode after just a few months? Low-quality materials lead to frequent failures and safety risks. What should you look for in a durable cartridge heater?
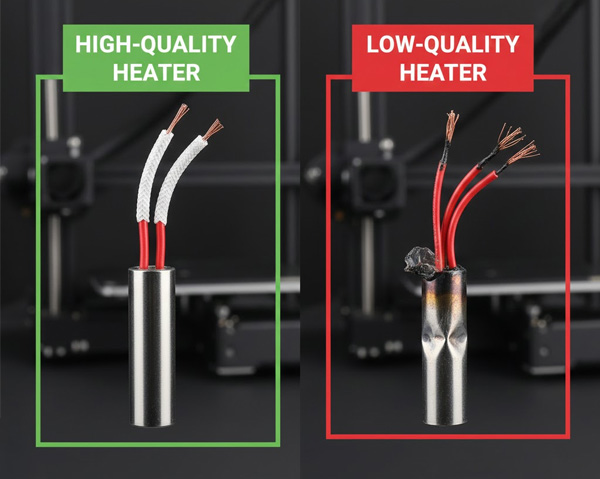
A reliable 3D printer cartridge heater features a durable 304 stainless steel casing and high-temperature fiberglass lead wires. This construction ensures it can withstand prolonged exposure to temperatures up to 250°C and beyond. Cheaper materials like nylon wires will quickly degrade under heat.
The Difference High-Quality Materials Make
I have seen countless failures caused by cheap components. A few years ago, a budget heater I was testing had its nylon lead wires melt and short out after only a month of use. It taught me a valuable lesson: sacrificing quality for a few dollars costs far more in the long run. High-temperature applications demand robust materials.
The materials used in your cartridge heater directly impact its lifespan and safety.
304 Stainless Steel Casing
The outer casing should be made from 304 stainless steel. This material offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand the high temperatures found in 3D printer hotends. It resists oxidation and maintains its structural integrity over time. Cheaper alternatives might use lower-grade stainless steel or even mild steel. These can corrode, warp, or crack under constant thermal cycling. This leads to poor heat transfer and eventual failure. Our tubular heaters and casting heaters, designed for diverse industrial applications, use high-grade materials for maximum durability and performance, even in extreme conditions.
High-Temperature Fiberglass Lead Wires
The lead wires are equally important. They must be insulated with high-temperature fiberglass. This material can comfortably handle temperatures exceeding 250°C without degrading. Regular PVC or nylon insulation, found on cheaper heaters, will quickly become brittle, crack, melt, or short out when exposed to the sustained heat near the hotend. This is a significant safety hazard. Always look for braided fiberglass insulation on the lead wires. This ensures electrical integrity and safety over the life of the heater.
Internal Construction
Beyond the visible parts, the internal components also matter. A high-quality heater will have a precisely wound resistance coil, securely packed with magnesium oxide (MgO) insulation. MgO provides excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, ensuring efficient and safe operation. Poorly packed or low-grade insulation can lead to hot spots, uneven heating, and premature failure.
Material Checklist for Your Heater
- Casing: 304 Stainless Steel (minimum)
- Lead Wires: High-Temperature Fiberglass (braided)
- Internal Insulation: High-Purity Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Investing in a heater with these material specifications ensures reliability, safety, and consistent performance for your 3D printing setup.
Conclusion
Choosing the right 3D printer cartridge heater is simple when you focus on key specifications: diameter, length, wattage, voltage, and materials. Matching these ensures efficient heating, reliable operation, and high-quality 3D prints every time.