An Engineer's Guide to Finned Tubular Heaters
Hello, I'm an engineer here at Elekheat. I've spent over two decades working with heating elements, from the design phase to seeing them perform in the field. Today, I want to talk about one of the most versatile and efficient solutions we manufacture: the finned tubular heater.
Many of our clients, from OEMs to MRO technicians, come to us looking for a reliable way to heat air or other gases. The finned heater is often the perfect answer. Its design is simple but incredibly effective. It takes a standard tubular heater and dramatically increases its surface area by adding fins. This small change makes a huge difference in performance, especially in applications that require forced convection.
Article Directory
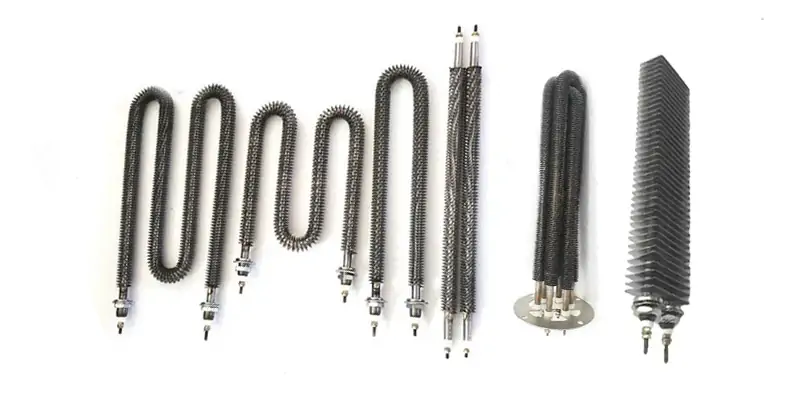

What Exactly is a Finned Tubular Heater?
A finned tubular heater is an electric heating element that converts electrical energy into heat. The core concept is straightforward. We take a standard tubular heating element and attach a series of metal fins to its outer sheath.
These fins act like a radiator on a car. They expand the surface area that comes into contact with the surrounding air or gas. This design allows the heater to transfer heat much more efficiently than a plain-sheath element of the same size. The result is that we can achieve higher power outputs in a smaller package, or run the element at a lower surface temperature for a longer lifespan.
Dive Deeper: The Core Components
Let's break down what goes into one of our finned heaters. At the heart is a high-resistance nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloy wire. This is the component that actually generates the heat when electricity passes through it. This wire is carefully coiled and centered inside a high-quality stainless steel or Incoloy® tube, which we call the sheath.
To ensure safety and performance, the space between the coil and the sheath is filled with compacted magnesium oxide (MgO) powder. The MgO is a fantastic electrical insulator but an excellent thermal conductor. This means it prevents any electrical shorts while efficiently transferring the heat from the coil to the sheath.
Finally, we attach the fins, usually made of stainless steel or aluminum, to the sheath. We use a high-pressure mechanical process or brazing to ensure a solid bond. This bond is critical for effective heat transfer; any gaps would trap air and reduce efficiency. Every material is chosen for its specific properties to ensure a long, reliable service life, even in demanding industrial environments.
How Does a Finned Heater Work?
The working principle is based on fluid dynamics and thermodynamics. A cool fluid, typically air, is forced to flow across the heater. This is usually done with a fan or blower in applications like duct heaters or forced-air ovens. As the air passes over the fins, it absorbs the heat generated by the element.
The path of the airflow is specifically designed to maximize contact time and turbulence, ensuring the most effective heat exchange. The heated air then moves out of the system to do its job, whether that's drying parts, curing coatings, or simply heating a space. An integrated control system, often using a temperature sensor at the outlet, continuously monitors the air temperature. It adjusts the power output of the heater to maintain a consistent, uniform temperature as required by the process.
Why Choose a Finned Heater Over a Standard One?
The primary advantage is the significantly increased heat dissipation area. The fins expand the surface area by 2 to 3 times compared to a standard tubular element. This means a finned element can handle a surface power load that is 3 to 4 times higher. In practical terms, this gives you several key benefits:
- Faster Heat-Up Times: With more surface area, heat is transferred to the air more quickly.
- Higher Efficiency: The element operates at a lower surface temperature for the same power output, which reduces heat loss and extends its lifespan.
- Compact Design: You can get more heating power from a smaller unit, saving valuable space in your equipment.
- Lower Cost: In many cases, a smaller, more efficient finned heater can be more cost-effective than a larger array of standard elements.
Compare Heater Performance
See the difference in surface area for yourself. Enter the length of a standard heater to see how adding fins increases its effective heating surface.
| Heater Type | Approx. Surface Area (mm²) | Relative Power Load |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Tubular Heater | 1x | |
| Finned Tubular Heater | ~3x - 4x |
Dive Deeper: A Real-World Application Story

I remember working with a purchasing manager from a large food processing plant. They were struggling with inconsistent results and high energy bills in their convection oven. Their oven used a bank of standard tubular heaters, and the MRO team was replacing them frequently because they were running too hot.
After analyzing their setup, we proposed a custom-designed array of our finned tubular heaters. The new elements had the same total power output but operated at a much lower sheath temperature. The installation was straightforward. The results were immediate: their heat-up times dropped by 20%, energy consumption decreased by nearly 15%, and product quality became perfectly uniform. Most importantly, element failures became a rare event instead of a weekly headache. It was a perfect example of how choosing the right component can impact the entire production line.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What materials are used for the fins and sheath?
We typically use high-quality stainless steel (like 304 or 316) for both the sheath and the fins because of its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. For very high-temperature applications or specific chemical environments, we might use Incoloy® or other specialized alloys. The choice always depends on the specific operating conditions of your application.
Can finned heaters be customized?
Absolutely. This is one of our core strengths at Elekheat. Since our founding in 1997, we've specialized in creating custom solutions. We can design heaters in various shapes (straight, U-bent, or complex forms), lengths, diameters, and with different fin spacings and materials to perfectly match your equipment and process requirements.
What industries use finned heaters?
Their versatility makes them popular across many sectors. We supply them to HVAC manufacturers for duct heating, to food processing plants for convection ovens and dryers, and to industrial machinery OEMs for applications like plastic curing and heat treating. You'll also find them in chemical plants, textile manufacturing, and even in home appliances. Anywhere you need to heat moving air efficiently, a finned heater is a great choice.
Consolidation: Your Reliable Heating Partner
To sum it up, the finned tubular heater is a robust, efficient, and cost-effective solution for a wide range of air and gas heating applications. Its key advantage lies in the expanded surface area, which allows for faster heating, better efficiency, and a longer service life.
At Elekheat, we combine state-of-the-art manufacturing with decades of engineering experience to provide you with not just a component, but a complete heating solution. Explore our range of finned tubular heaters on our product page or contact our engineering team to discuss your specific needs. We are here to be your long-term partner, ensuring your processes run smoothly and efficiently.

