Finned Heaters: Essential Guide
Finned Heaters: The Essential Guide to Efficient Industrial Heating
Finned heaters are versatile electric heating elements designed for efficient heat transfer, especially for air and gases. They provide precise temperature control for various industrial applications. This guide covers their function, components, benefits, uses, and installation.

Article Summary
What Are Finned Heaters?
Finned heaters are electric heating elements with metal fins attached to their sheath. These fins significantly increase the surface area, making them highly effective for heating air or gases through forced convection. They ensure precise, rapid, and uniform temperature control.
How They Work:
An electrical resistance element generates heat, which conducts through magnesium oxide insulation to the metal sheath. The fins then efficiently transfer this heat to the flowing air or gas, ensuring quick and even heating.
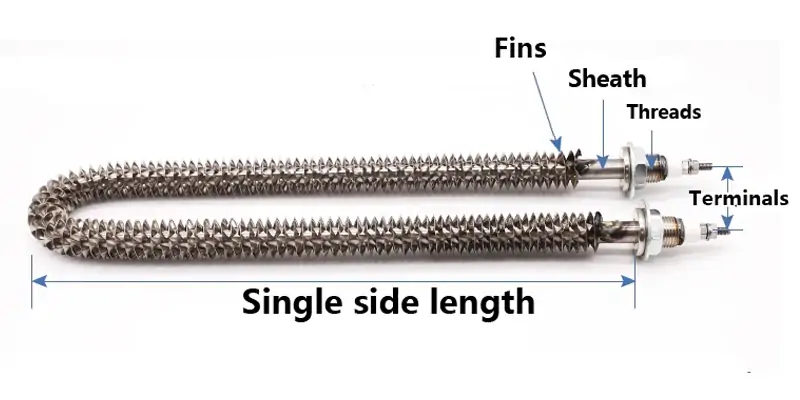
Key Components and Materials
Understanding the components helps appreciate their performance and durability.
The Heating Element:
A nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloy coil converts electricity to heat efficiently, ensuring uniform heat and long life.
The Sheath:
The metal sheath protects the element and transfers heat. Material choice depends on operating temperature and environment:
- Steel: For air, oils, asphalt, molten salt (up to 850°F/454°C).
- Copper: For clean water (up to 350°F/177°C).
- Stainless Steel (304SS, 316SS): Durable, corrosion-resistant, for humid/corrosive atmospheres (up to 1200°F/649°C).
- Incoloy (800, 840): High-temperature, oxidation, and corrosion resistance (up to 1600°F/871°C).
- Specialized Alloys (Monel, Inconel, Titanium): For extreme corrosive or high-temperature uses.
Fins:
Made from steel, stainless steel, or aluminized steel, fins greatly increase surface area for heat transfer. They are attached by brazing (for strong bond) or mechanical winding, with various designs for specific needs.
Magnesium Oxide (MgO):
This compacted powder insulates electrically and conducts heat efficiently from the element to the sheath, preventing short circuits and ensuring heat transfer.
Why Choose Finned Heaters? Key Advantages
Finned heaters offer significant benefits for industrial applications:
- High Efficiency: Superior heat transfer, lower energy use.
- Lower Operating Temperatures: Higher power output with extended lifespan.
- Compact Design: High power in a smaller footprint.
- Uniform Heating: Consistent temperature control, no hotspots.
- Versatility & Customizability: Adaptable to various shapes, sizes, and media.
- Durability & Reliability: Robust construction, long service life, low maintenance.
- Enhanced Safety: Encased element minimizes fire and shock risks.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower long-term energy and maintenance costs.
Common Applications Across Industries
These heaters are vital in many sectors due to their versatility and durability:
- HVAC Systems: Air duct and space heating.
- Industrial Ovens & Dryers: Curing, baking, annealing, drying.
- Food & Beverage: Processing lines, commercial ovens.
- Chemical Industry: Heating materials, drying powders, hazardous environments.
- Oil & Gas: Heating hydrocarbons, process fluids.
- Plastics Industry: Injection molding, extrusion, mold heating.
- Automotive & Aerospace: Engine heaters, defrosting, curing composites.

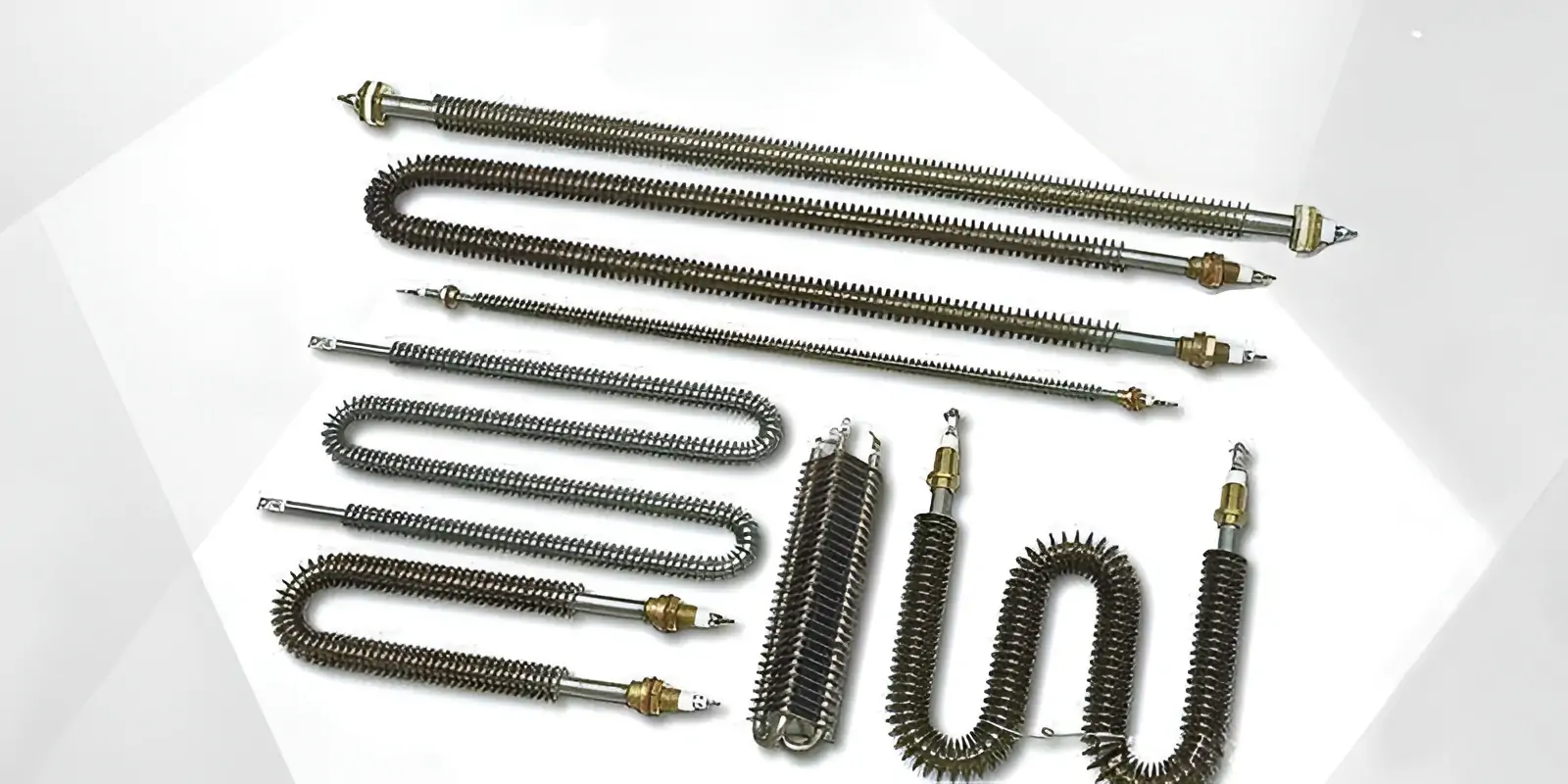
Diverse Product Forms and Shapes
Finned heaters come in many shapes to fit specific equipment and space limitations.

Straight Elements
Linear form for duct heaters or radiant heating.

U-Shaped Elements
Common for duct heaters where terminals are at one end.

M-Shaped Elements
Increases heated length in a compact area, often for ovens.

Coiled / Helical Forms
Maximizes heated surface area in cylindrical spaces.

Flanged Assemblies
Multiple elements on a flange for easy duct or vessel installation.

Custom Bends
Tailored to fit unique equipment designs.
Heat Load Calculator (Air Heating)
Estimate the wattage required to heat a specific volume of air to a desired temperature.
Calculate Required Wattage
Required Wattage:
Formula: Watts = CFM × 0.317 × ΔT
Technical Specifications
Key specifications for proper selection and sizing:
Standard Finned OD & Fin Specs
| Sheath Dia. (in) | Fin Width (in) | Fins/Inch | Finned OD (in) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.315 | 5/16 | 5±0.5 | 0.92 |
| 0.375 | 3/8 | 5±0.5 | 1.11 |
| 0.430 | 3/8 | 5±0.5 | 1.16 |
| 0.475 | 3/8 | 5±0.5 | 1.21 |
Electrical Limits by Sheath Dia.
| Sheath Dia. (in) | Max. Voltage | Max. Amps |
|---|---|---|
| 0.260 | 250V | 20A |
| 0.315 | 300V | 30A |
| 0.375 | 480V | 40A |
| 0.475 | 600V | 40A |
Comparative Analysis with Other Heaters
Compare different heater types based on performance and application using the interactive tool below.
Heater Comparison Tool
| Pros | |
| Cons | |
| Best For |
Installation Guide
Proper installation ensures safe and efficient operation. Always refer to manufacturer manuals for detailed instructions.
Mechanical Installation
- Mounting: Securely mount using compatible fittings to prevent movement.
- Airflow: Ensure adequate and uniform airflow across fins to prevent overheating.
- Clearance: Maintain proper clearance for thermal expansion.
- Vibration: Minimize vibration to prevent fin loosening.
- Contaminants: Periodically clean fins in dusty environments.
Electrical Installation
- Personnel: Only qualified electricians should perform electrical connections.
- Voltage & Amperage: Match supply to heater specifications.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding for safety.
- Wiring: Use high-temperature rated, securely connected wiring.
- Controls: Integrate with thermostats and safety devices.
Real-World Case Studies
Automotive Curing Oven
Challenge: Uneven heating and high energy use in a paint curing oven.
Solution: Custom U-shaped Incoloy 840 finned heaters with precise airflow controls.
Results: 15% shorter curing time, 20% energy savings, and enhanced paint quality.
HVAC Duct Heating
Challenge: Achieving rapid, uniform heating in a large commercial building's HVAC system.
Solution: Modular steel-finned heater assemblies with multiple control zones.
Results: Improved comfort, significant energy savings, and reduced maintenance.
Industrial Food Drying
Challenge: Inconsistent product quality and high energy costs in a food drying process.
Solution: Stainless steel finned heaters in a recirculating hot air dryer.
Results: Consistent quality, 30% energy cost reduction, and increased throughput.
Product FAQ
Conclusion
Finned heaters are a vital industrial heating technology, offering high efficiency, robust design, and extensive customization. Their unique finned structure excels in air and gas heating, providing superior heat transfer and energy savings. With diverse materials, shapes, and installation options, they integrate precisely into various processes. For businesses seeking energy efficiency and reliable temperature control, the finned heater is a smart long-term investment.





