The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Immersion Heaters
Last updated: July 2025
Welcome to the definitive **immersion heater guide** for engineers, technicians, and procurement managers. **Industrial immersion heaters** are a cornerstone of modern process heating, offering unparalleled efficiency and precision. However, achieving optimal performance and longevity depends on critical factors like correct **immersion heater sizing** and selecting the appropriate **watt density** for your specific fluid. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of everything you need to know, from heater types and material selection to maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring you can specify the perfect heater for your application.
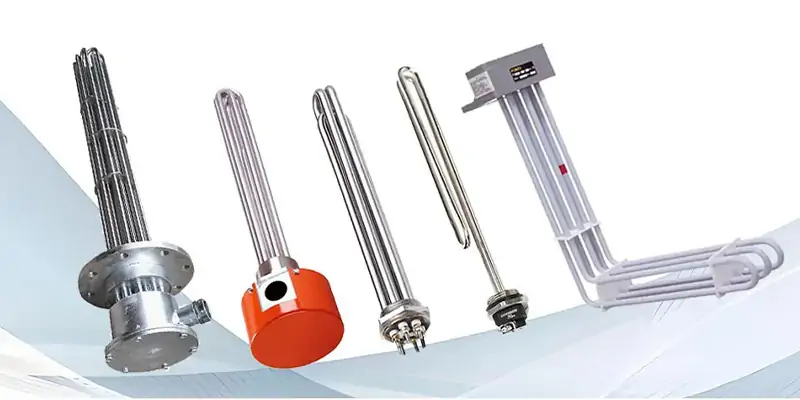

What Is an Immersion Heater?
An industrial immersion heater is a high-powered electric heating device designed to be directly submerged in a liquid to heat it. By converting electrical energy into thermal energy within the fluid itself, it achieves nearly 100% efficiency. These heaters are used across various industries to heat water, oils, solvents, and chemical solutions in tanks, vessels, and pipes, making them essential for processes that require precise and reliable temperature control.
The Foundational Guide to Industrial Immersion Heating
The primary advantage of electric immersion heating lies in its method of heat delivery. Immersion heaters are designed to be submerged directly into the fluid, where direct contact ensures that virtually all electrical energy is converted into usable heat, resulting in energy efficiency approaching 100%.
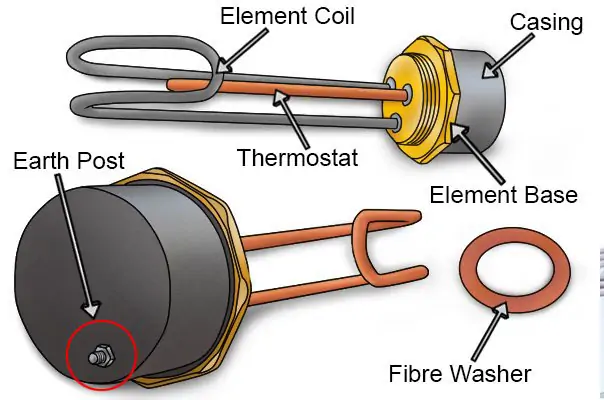
Anatomy of an Immersion Heater
- Heating Element: The core, typically a nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloy wire, which generates heat via electrical resistance.
- Sheath: The protective outer tube that houses the element and transfers heat. Its material (e.g., copper, steel, Incoloy) is chosen based on the fluid's properties.
- Terminal Enclosure: A protective housing for electrical connections, rated by NEMA for the specific operating environment (e.g., NEMA 4 for moisture resistance, NEMA 7 for hazardous locations).
A Comparative Analysis of Immersion Heater Architectures
Immersion heaters are engineered into distinct configurations, each offering a unique combination of power, pressure capability, and installation method.
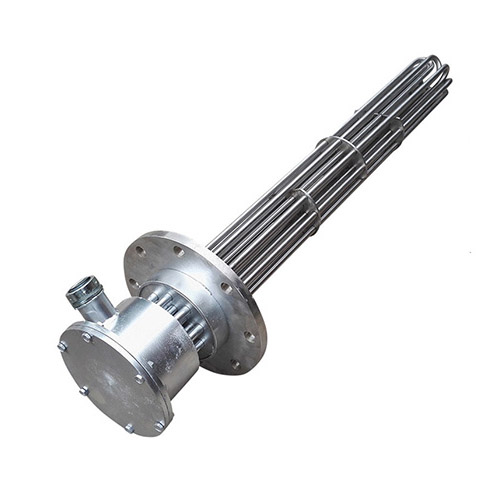

Flanged Immersion Heater
The workhorse for high-power, high-pressure applications. Multiple elements are mounted on a standard ANSI flange for direct installation into tanks and pressurized vessels.
Ideal for: Large tanks, boilers, chemical reactors, crude oil.
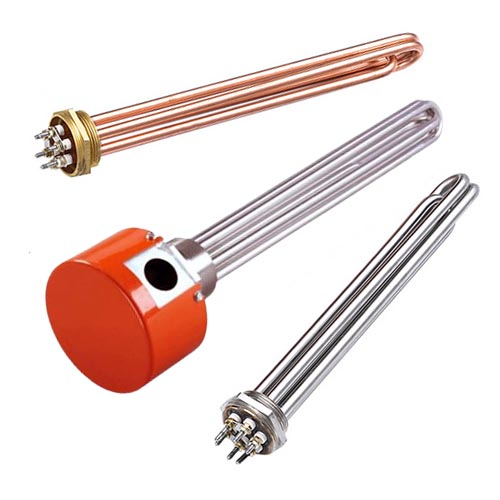

Threaded Immersion Heater (Screw Plug)
Compact, versatile, and easily installed. Elements are mounted into a threaded plug for direct immersion in smaller tanks and reservoirs.
Ideal for: Process water, freeze protection, oil heating, labs.
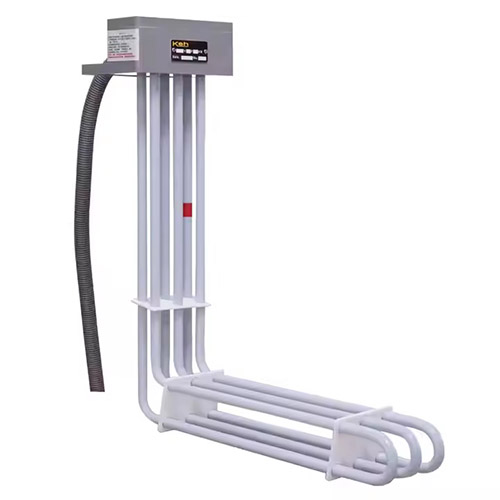

Over-the-Side Heater
Portable and non-invasive. This over-the-side heater hangs over the edge of open tanks, requiring no tank modifications. Perfect for retrofitting and temporary use.
Ideal for: Plating baths, cleaning solutions, open-tank heating.
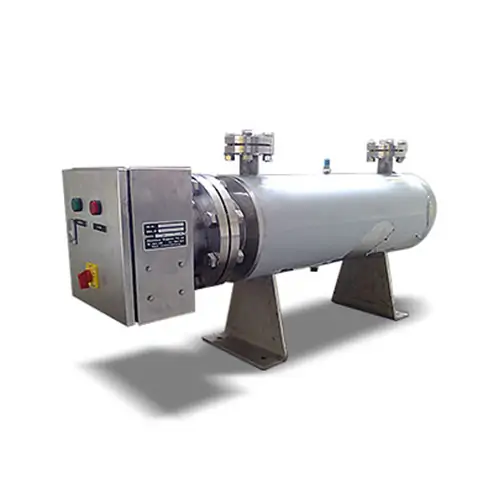

Circulation Heaters
The pinnacle of process control. An immersion heater is mounted in an insulated chamber for heating flowing liquids or gases with maximum efficiency and precision.
Ideal for: Heat transfer fluids, fuel oil, gas heating, in-line processes.
The Engineer's Handbook for Immersion Heater Specification
Correctly specifying an immersion heater involves a series of critical engineering decisions that determine its performance, safety, and operational lifespan.
Interactive Sizing Calculator
Calculate Required Kilowatts (kW)
Required Power (Minimum)
61.0 kW
Sheath Material Selection: A Detailed Comparison
The sheath material is the heater's first line of defense against corrosion. Choosing a material that is chemically compatible with the fluid is non-negotiable for ensuring a long service life.
| Sheath Material | Resistance Rating | Ideal For | Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Fair | Clean water, non-corrosive solutions | Acids, deionized water, ammonia |
| Steel | Good | Oils, tars, heat transfer fluids | Most acids, corrosive solutions, water |
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | Excellent | Process water, mild corrosives, food-grade applications | Hydrochloric acid, chlorides, sulfides |
| Incoloy® 800/840 | Superior | High-temperature air, sulfide-bearing solutions, hard water | Strongly oxidizing acids |
| Titanium | Superior | Chlorine solutions, seawater, nitric acid, most plating baths | Hydrofluoric acid, strong reducing acids |
| PTFE (Teflon™) | Exceptional | Virtually all acids and aggressive chemicals | Applications requiring high watt density |
Understanding Thermostat and Control Options
The control system regulates temperature and ensures safe operation. The choice between a simple mechanical thermostat and a precise digital controller depends entirely on the application's requirements for accuracy.

Capillary Thermostats
These are mechanical controllers that use the expansion and contraction of a fluid in a bulb and capillary tube to operate a switch. They are robust and cost-effective.
- Accuracy: Typically ±5°C
- Best For: General purpose applications where precise temperature is not critical, such as freeze protection or basic water heating.

Digital Thermostats & Controllers
These electronic controllers use sensors like thermocouples or RTDs to provide real-time temperature feedback, allowing for much tighter control.
- Accuracy: Can be as precise as ±1°C or better.
- Best For: High-precision processes, chemical reactions, laboratories, and any application where temperature stability is critical to product quality.
Navigating Certifications and Safety Standards
Third-party certifications provide independent verification that a product meets established standards for safety and reliability. For industrial customers, these certifications are often a mandatory procurement requirement.
- UL 499 (Commercial & Industrial Use): This is the key safety standard from Underwriters Laboratories for electric heating appliances in the North American market. Compliance with UL 499 signifies that a heater has undergone rigorous testing for electrical safety, construction, and performance, making it suitable for demanding commercial and industrial environments.
- IEC/EN 60335-2 (Household Use): It is important to distinguish industrial-grade heaters from those intended for residential use. Standards like IEC/EN 60335-2 apply to household appliances and have different requirements. Elekheat products are built to robust industrial standards like UL 499, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of continuous industrial operation.

UL 499 Certification for Commercial Use

IEC/EN Certification for Safety
Immersion Heaters in Action: A Cross-Industry Application Matrix
From purifying water to refining crude oil, immersion heaters provide the precise thermal energy required for countless critical processes.
| Industry | Application | Recommended Heater & Sheath |
|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Freeze protection, process optimization | Screw Plug or Flanged; Stainless Steel |
| Petrochemical | Preheating crude oil, viscosity reduction | Flanged or Circulation; Steel |
| Electroplating | Heating acidic and alkaline plating baths | Over-the-Side; Titanium or PTFE |
| Food & Beverage | Heating process water and vegetable oils | Screw Plug; Food-Grade Stainless Steel |
Solutions for Your Entire Team
We understand that a heater is a critical asset. We design our products and provide support to meet the distinct needs of the engineers who design the process, the managers who maintain it, and the agents who procure it.
For the Process Engineer
Get the performance, reliability, and compliance your system design demands with detailed technical data and expert consultation.
For the Maintenance Manager
Maximize uptime with heaters designed for durability and easy service, backed by clear troubleshooting guides.
For the Purchasing Agent
Invest in long-term value. Our heaters deliver a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) through superior efficiency and longevity.
Maximizing ROI: A Framework for Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The purchase price is only a fraction of a heater's true cost. TCO provides a comprehensive financial framework for evaluating assets by including operating, maintenance, and downtime costs.
TCO Comparison: Electric Immersion vs. Gas-Fired Boiler
While gas boilers may have a lower initial price, a TCO analysis over a 15-20 year lifespan often reveals that the superior efficiency and dramatically lower maintenance costs of an electric immersion system make it the more cost-effective choice.
| Cost Component | Electric Immersion Boiler | Gas-Fired Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost (I) | €100,000 | €80,000 |
| Efficiency | ~99% | ~75% |
| Operating Cost (O) | €575,000 | €700,000 |
| Maintenance Cost (M) | €80,000 | €200,000 |
| Total Cost of Ownership | €755,000 | €980,000 |
*This is a hypothetical calculation. Actual figures will vary based on local energy prices, usage patterns, and specific equipment.
A Practical Field Guide: Installation, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting
Correct installation and diligent maintenance are key to ensuring heater longevity, maximizing efficiency, and minimizing costly, unplanned downtime.
Video Guide: Immersion Heater Installation & Maintenance
| Symptom | Potential Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No Heat; Breaker Tripped | Shorted heating element or wiring | Test element with a multimeter. Replace heater if shorted. |
| Slow Heating | Scale/sludge buildup or partial element failure | Remove and clean elements. Test each element for continuity. |
| Heater Overheating | Low liquid level or severe scale buildup | Shut off power immediately. Refill tank and clean/replace heater. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the watt density in immersion heaters?
Watt density is the heater’s power output in watts per square inch of its surface area (W/in²). It is a critical factor for ensuring the heater does not damage the fluid it is heating. For example, water can handle a high watt density, while thick oils require a very low watt density to prevent scorching and coking.
How long do immersion heaters last?
The lifespan of an industrial immersion heater typically ranges from 5 to 10 years, but this is highly dependent on several factors: selecting the correct watt density for the fluid, choosing a sheath material that resists corrosion, and performing regular immersion heater maintenance to prevent scale or sludge buildup.
Can immersion heaters be used with oils?
Yes, immersion heaters are commonly used with oils, but it is critical to use a heater with a low watt density. High watt densities will burn (or 'coke') the oil onto the heater surface, causing the heater to overheat and fail. Steel sheaths are typically used for non-corrosive oils.
What’s the difference between flanged and screw plug types?
A flanged immersion heater is a high-power unit designed to be bolted onto large tanks or pressurized vessels. A screw plug (or threaded) immersion heater is more compact and is screwed into a threaded opening, making it ideal for smaller tanks and applications.
Is it safe to run an immersion heater dry?
No, it is extremely dangerous. An immersion heater must be fully submerged during operation. Running a heater dry will cause the element to overheat and burn out within minutes, creating a significant fire hazard and permanently damaging the equipment. A low-liquid level cutoff switch is a critical safety feature to prevent this.
How often to replace heating elements?
Heating elements are integral to the heater assembly and are not typically replaced individually. If a single element fails (e.g., develops a short or open circuit), the entire immersion heater unit is replaced. With proper specification for the application (correct watt density and sheath material) and regular maintenance, a heater should provide a service life of 5-10 years or more.
Can I use an immersion heater with corrosive liquids?
Absolutely, but you must select the correct sheath material to prevent rapid failure. For highly corrosive solutions like acids and aggressive plating baths, specialized materials are required. Materials like Titanium and PTFE (Teflon™) are designed specifically for these harsh environments. Using a standard steel or copper heater in an acid would result in almost immediate failure.
Ready to Improve Your Process Heating?
Let's talk about your specific application. Our engineers are ready to help you select the right immersion heater to improve your efficiency, reduce downtime, and lower your total cost of ownership.




